How to use Jupyter Notebooks
The power of Python
Jupyter Notebook is an open-source web application for creating and sharing documents containing live code, mathematical formulas, visualisations, and text. This is a great tool to develop and present code in a standardised text block format that is interactive and shareable. You can create code, mathematical formulas, data visulaisations, and even freestyle text-all in Jupyter notebooks!
You will be using Jupyter notebooks to write, execute, and present your own code throughout this program. This reading will guide you through using your own notebook.
Jupyter Notebook
You can access Jupyter Notebook directly from your browser or download the desktop application onto your device to work with over 100 programming languages, including some you might already know like R and Python. There is JupyterLab, which is the full suite of tools for working with computational notebooks. There is also Jupyter Notebook, which is a more streamlined and simplified tool that nonetheless offers powerful ways to perform interactive computing. Again, for this certificate program, we recommend working within the Jupyter Notebook interface provided by Coursera. Activities that use Jupyter notebooks will be labeled as labs, and you will find relevant instructions for each activity on its landing page.
Why Juypter Notebook?
Notebooks are particularly useful for workig with data. Here are some ways that Jupyter notebooks excel:
-
Modular/interactive computing: You can write and execute individual chunks of code in small, manageable chunks, which are called cells. You can run a cell without necesarily having to run the whole notebook. This is sepecially helpful for data exploration and experimentation. Cells are also helpful with debugging, becuase they provide a user-friendly way to make a mistake, notice that you made the mistake, and iterate back to correct your mistake, without having to re-execute a whole script.
-
Integration of code and documentation: Notebooks allows you to combine code, textual explanations, and visualisations like charts, graphs, and tables-all in a single document.
-
Support for multiple languages: The Advanced Data Analytics program will use Python, but Jupyer notebooks support many other languages, making them powerful and versatile.
-
Data exploration and analysis: The notebook simplifies working with data by offering tools to load, clean, analyse, and examine it in an elegent interface.
-
Cloud-based services: Many cloud computing platforms host Jupyter notebooks, which makes it easy to run and share notebooks without setting up a local environment. This is very useful for collaboration.
-
Libraries and extensions: There is a rich ecosystem of extensions and plugins that enhance functionality for whatever type of project you’re working on.
How to use Jupyter notebooks
Once you’ve opened a Jupyter notebook, it’s time to use it! Here are some tips to get started.
Command/edit mode
Notebooks have two working modes: command mode and edit mode. Command mode is used to interact with the notebook as a whole and perform actions like adding, moving, and deleting cells. Edit mode is used to type code or markdown text into a particular cell.
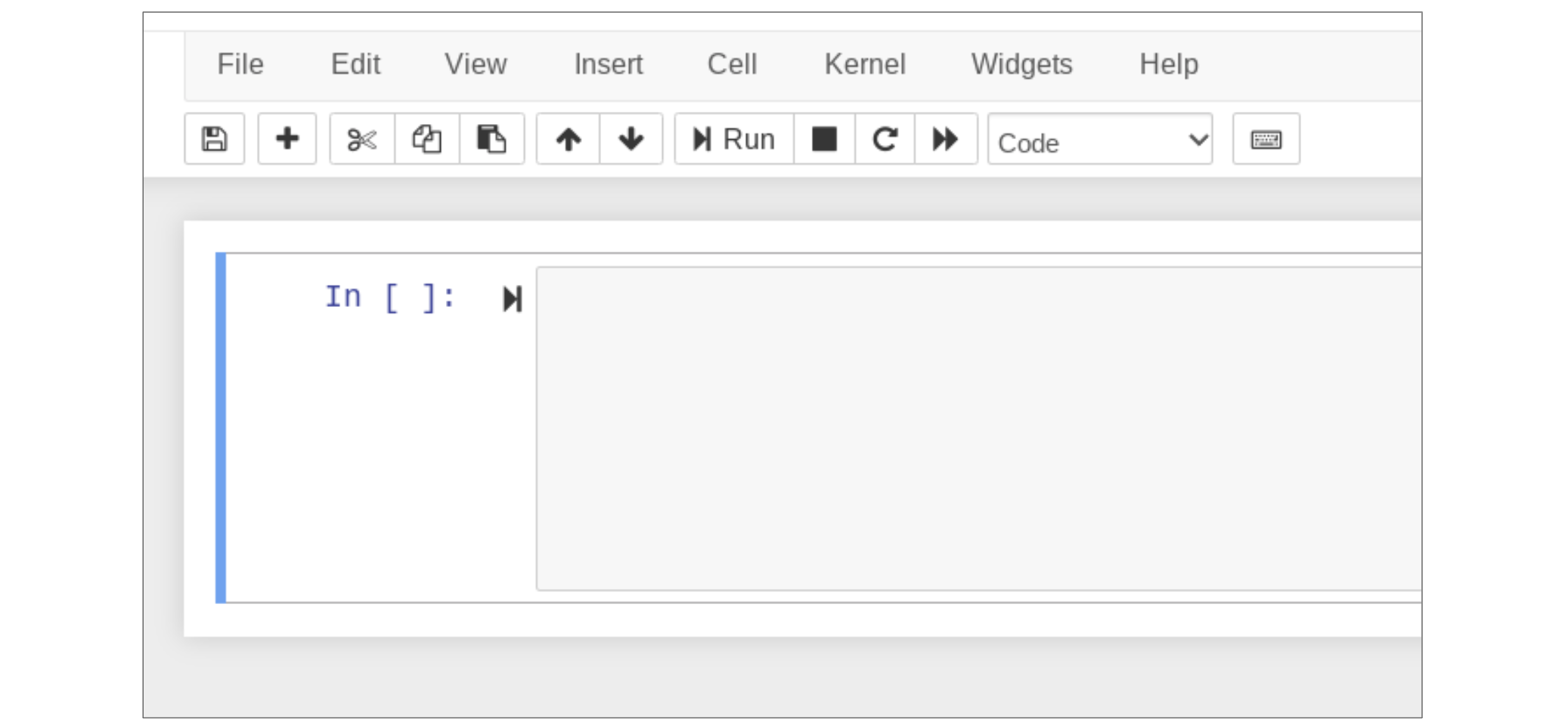
Command mode is indicated by a blue bar on the left side of the current cell.
Edit mode is indicated by a green bar on the left and also a thin green border around the active cell.
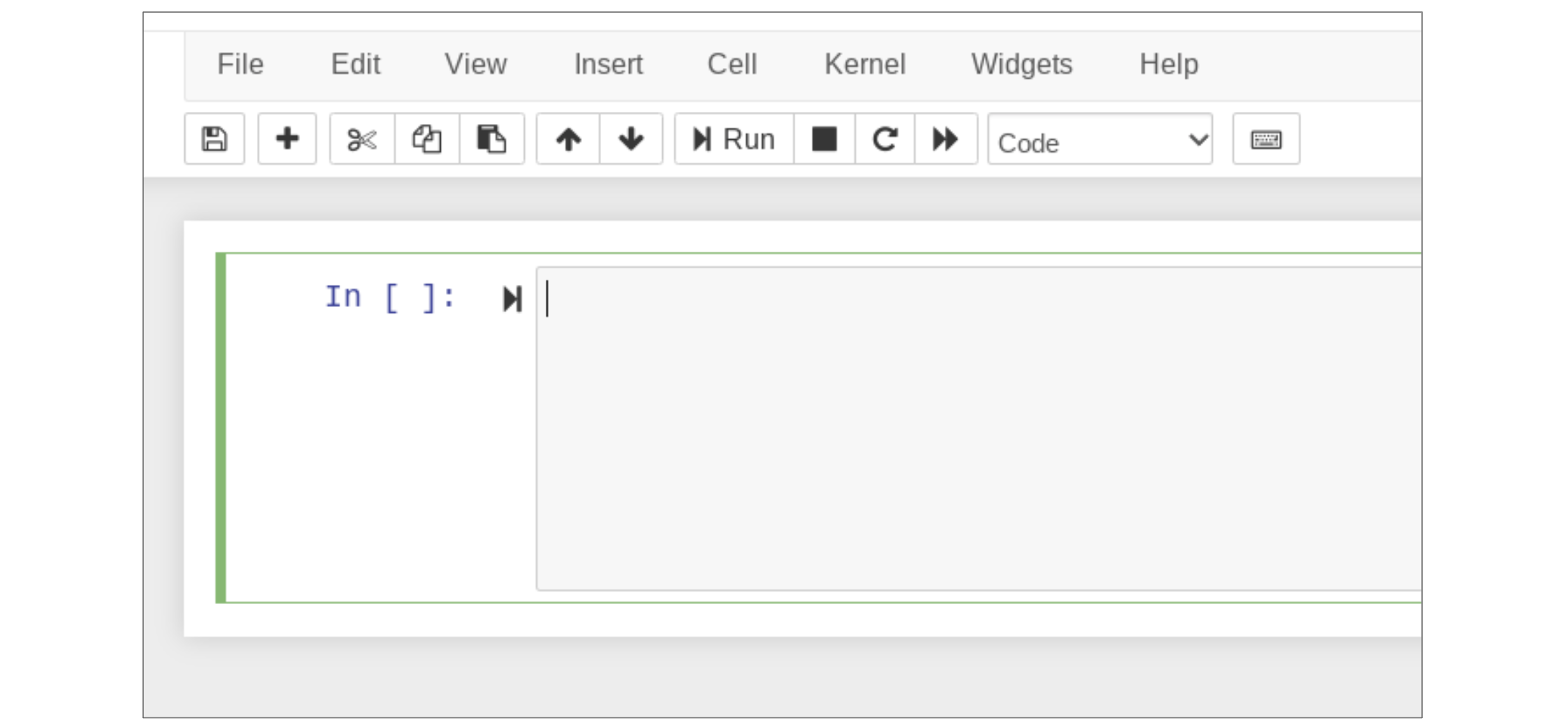
To enter into edit mode, simply click into a cell to insert your cursor there or use the navigation arrows on your keyboard to select a cell and press Enter. To revert back to command mode, click anywhere outside the cell or press the escape key.
Markdown mode
Jupyter notebooks allow you to toggle cells between coding mode and Markdown mode. Markdown is a markup language that lets you add formatting elements to plain text. It’s useful because it’s ubiquitous, future-proof, and platform independent. In Jupyter notebooks, Markdown text is used to provide written explanations, analysis, and context to explain the code and tis output. In the following example, all of the text above In [41]: was writeen and formatted using Markdown.
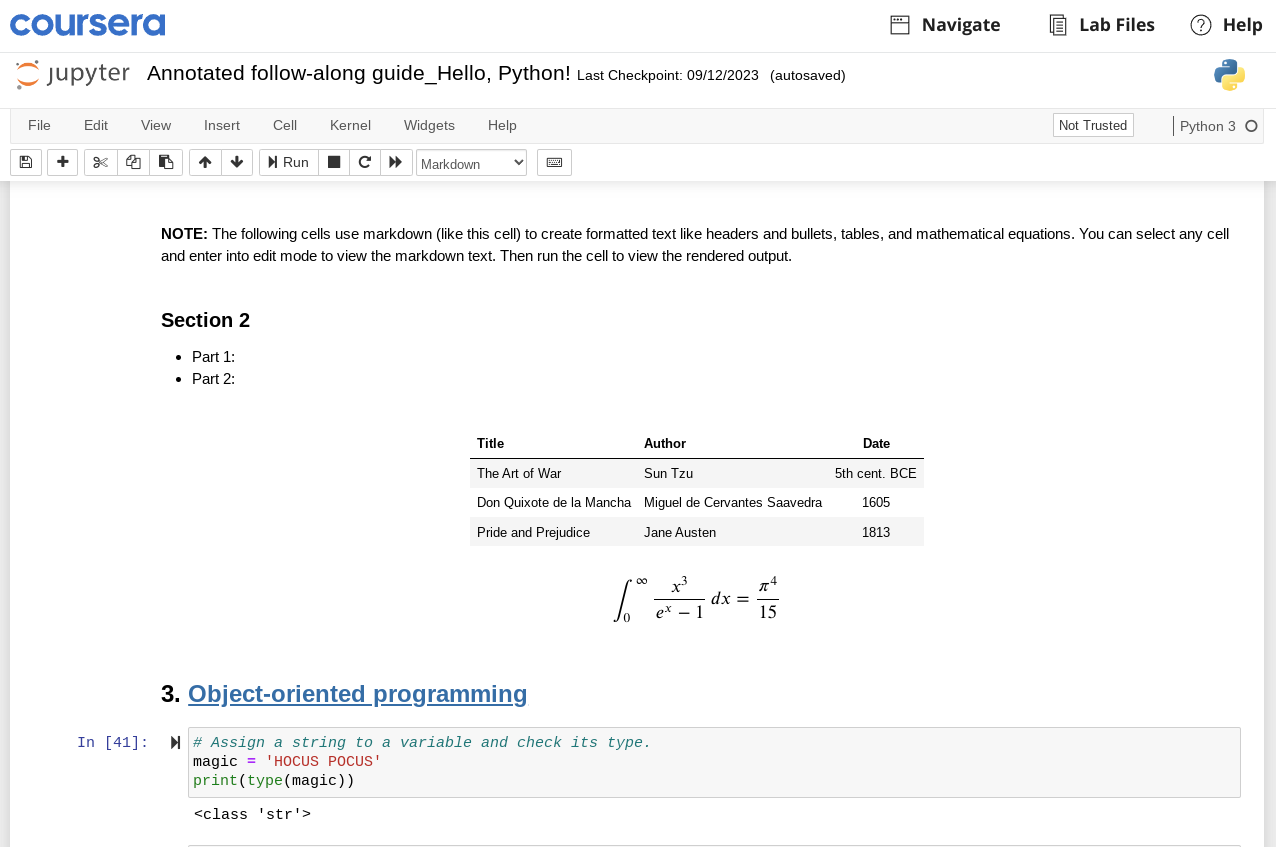
To toggle between code and Markdown mode, go to the menu at the top of the page and click where it says “Code.” Then, select “Markdown” from the dropdown menu that appears.
For more information about how to use Markdown, refer to Markdown guide for basic syntax and the Mark guide for extended syntax
Common actions
Most actions can be performed using both a mouse/graphic interface and keyboard shortcuts. Here are some of the most common actions.
Add a new cell
-
Click on Inster in the menu bar at the top of the notebook. Options are to insert a new cell above or below the current cell.
-
Keyboard shortcuts (while in command mode):
- a: Insert a cell above the crrent cell
- b: Insert a cell below the crrent cell
Delete a cell
- Use command mode to select a cell or group of cells.
- Click on Edit in the menu bar at the top of the notebook and select Delete Cells from the dropdown menu.
- Keyboard shortcut (while in commnad mode):
- dd(Press D two times)
Move a cell
-
Use command mode to select a cell or group of cells.
-
Click on the up arrow button or down arrow button in the menu bar at the top of the notebook to move the selected cell(s) up or down
Run a cell
-
Select a cell and click the Run button in the menu bar at the top of the notebook.
-
Keyboard shortcuts:
-
Command(⌘) + Enter: Run selected cell
-
Shift(⇧) + Enter: Run selected cell and select next cell
-
Option(⌥) + Enter: Run selected cell and insert new cell below
-
-
You can run cells from both command mode and edit mode
Press h while in command mode for a pop-up window with all available keyboard shortcuts. You can also check out Jupyter Notebook interface components for more detailed descriptions of various notebook features.
Troubleshooting
You will use Jupyter notebooks throughout the Advanced Data Analytics certificate program. At times, you might encounter difficulty accessing or running the notebook. Here are some troubleshooting steps to help you if this happens.
Browser compatibility
Make sure your internet browser is updated regularly. It is best to use the latest version of Google Chrome, Firefox, or Microsoft Edge. If your browser is outdated or you are using a browser that is not supported by Coursera, you may encounter a problem. If your browser is up to date and you are using one of the browsers listed above and still encountering problems, try restarting your browser or clearing your browser’s cache and cookies. You can also use incognito mode, which prevents your browser from storing cookies and other temporary data.
Internet connection
Coursera requires a stable internet connection. If you are experiencing problems starting or running a Jupyter notebook, your internet connection may be slow or unreliable. Some signs of an unstable internet connection may be pages failing to load, freezing labs, or the inability to type or enter commands within the lab environment.
Pro Tip: If you are unable to complete a lab on one device, try using another device.
Troubleshooting steps
To summarize, here are the troubleshooting steps to try if you encounter a problem with Jupyter notebooks in Coursera.
-
Make sure you are using the latest version of a supported browser: Google Chrome, Firefox, or Microsoft Edge.
-
Restart your browser and clear your browser’s cache and cookies. You can also use incognito mode.
-
Check your internet connection and make sure it is stable. You can try restarting your router and modem to regain a stable connection.
-
Try restarting the lab again.
If all this fails, it’s possible that Coursera is performing maintenance or experiencing a service interruption. In that case, wait a little while and try again.
Key takeaways
Jupyter Notebook provides a coding platform where you can develop and debug your own code. Knowing how to use and interact with notebooks will prepare you for upcoming activities where you will try out new Python skills and prepare for the end-of-course project. Python will be a great tool in your toolkit—it will open up more advanced analytics tools like machine learning and automated analysis. And, using Jupyter Notebook will be a great way to build your Python knowledge!
####Resources for more information